

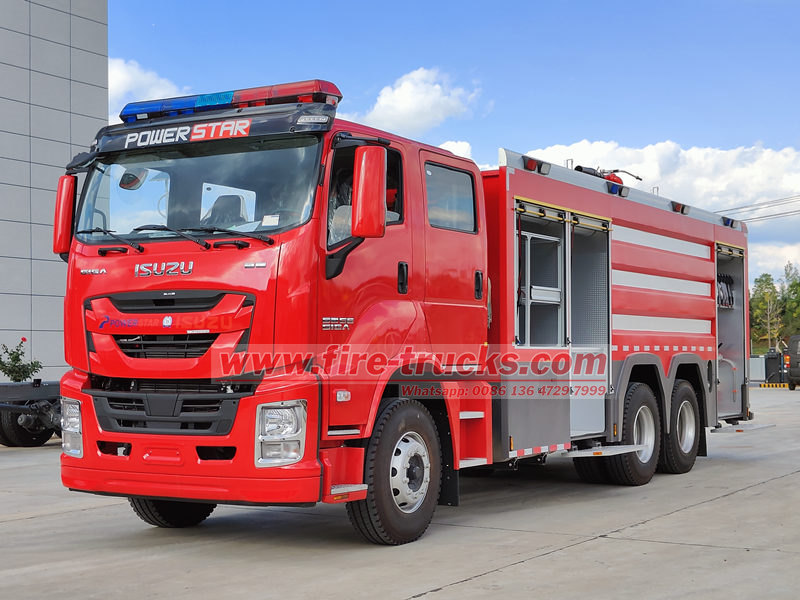
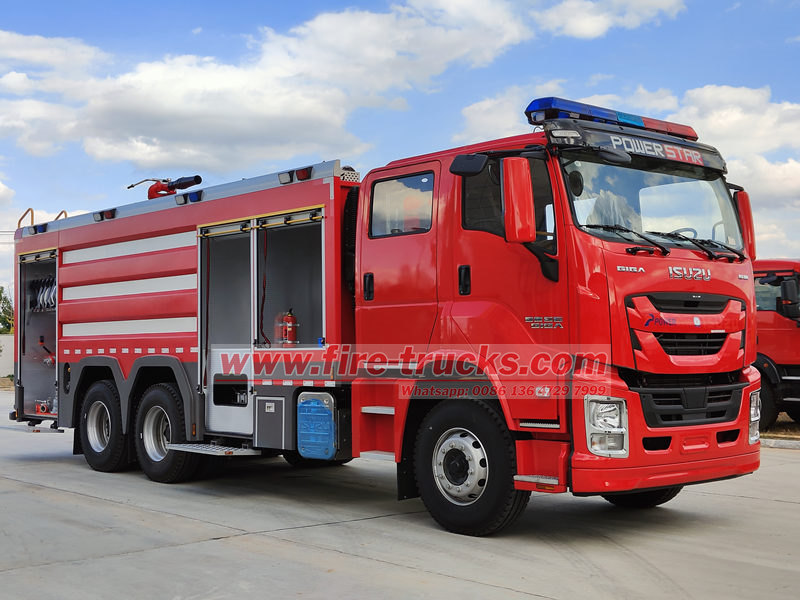
I camion antincendio ISUZU sono ampiamente riconosciuti nel settore antincendio globale per la loro affidabilità, efficienza e adattabilità. Essendo il componente principale di un camion antincendio, le prestazioni della pompa antincendio influiscono direttamente sull'efficienza antincendio. Camion dei pompieri ISUZU I camion antincendio ISUZU sono generalmente equipaggiati con vari modelli di pompe, come CB10/20, CB10/30, CB10/40, CB10/60, CB10/80 e CB10/100, per soddisfare diverse esigenze antincendio. Questo articolo fornisce un'introduzione dettagliata ai modelli di veicoli applicabili, ai principi di funzionamento e ai metodi di manutenzione di queste pompe antincendio, aiutando gli utenti a comprendere e utilizzare meglio i camion antincendio ISUZU.
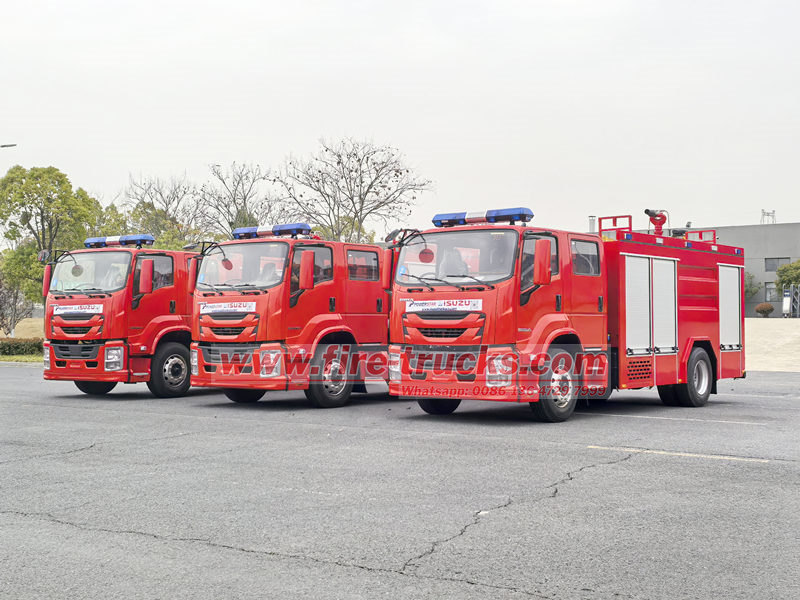

1. Modelli comuni di pompe antincendio per autopompe ISUZU e tipi di veicoli applicabili
I camion antincendio ISUZU sono dotati di pompe antincendio con specifiche diverse in base alla capacità di carico e ai requisiti funzionali. I modelli più comuni includono CB10/20, CB10/30, CB10/40, CB10/60, CB10/80 e CB10/100, dove i numeri rappresentano la portata (L/s) e la pressione (bar) della pompa. Ad esempio, CB10/40 indica una portata di 40 L/s e una pressione di 10 bar.
• CB10/20, CB10/30: adatti per autopompe ISUZU leggere (ad esempio, veicoli antincendio ISUZU NKR o NQR), utilizzati principalmente per la lotta antincendio nelle comunità e per la soppressione di incendi su piccola scala.
• CB10/40, CB10/60: comunemente presenti nei camion dei pompieri ISUZU di media portata (ad esempio, camion dei pompieri ISUZU FTR o FVR), adatti per la lotta antincendio urbana, la soppressione degli incendi nelle zone industriali e altri compiti ad alta richiesta.
• CB10/80, CB10/100: utilizzati principalmente nei camion dei pompieri ISUZU per impieghi gravosi (ad esempio, i camion dei pompieri ISUZU GIGA), progettati per incendi di grandi dimensioni, interventi antincendio in aeroporti e altri scenari ad alto flusso.
Parametri principali per la pompa antincendio:
[se gte mso 9]>
|
Model |
Work condition |
Flow rate (L/S) |
Outlet pressure (Mpa) |
Rated speed (r/min) |
Power (KW) |
Suction depth (m) |
|
CB10/20 |
1 |
20 |
1.0 |
3135±50 |
34 |
3 |
|
2 |
14 |
1.3 |
3440±50 |
35 |
3 |
|
|
3 |
10 |
1.0 |
3059±50 |
22 |
7 |
|
|
CB10/30 |
1 |
30 |
1.0 |
3010±50 |
48 |
3 |
|
2 |
21 |
1.3 |
3340±50 |
52 |
3 |
|
|
3 |
15 |
1.0 |
3000±50 |
34 |
7 |
|
|
CB10/40 |
1 |
40 |
1.0 |
3080±50 |
60 |
3 |
|
2 |
28 |
1.3 |
3360±50 |
61 |
3 |
|
|
3 |
20 |
1.0 |
2990±50 |
39 |
7 |
|
|
CB10/60 |
1 |
60 |
1.0 |
3200±50 |
102 |
3 |
|
2 |
42 |
1.3 |
3475±50 |
106 |
3 |
|
|
3 |
30 |
1.0 |
3130±50 |
73 |
7 |
|
|
CB10/80 |
1 |
80 |
1.0 |
3400±50 |
137 |
3 |
|
2 |
56 |
1.3 |
3500±50 |
130 |
3 |
|
|
3 |
40 |
1.0 |
3130±50 |
83 |
7 |
|
|
CB10/100 |
1 |
100 |
1.0 |
2270±50 |
149 |
3 |
|
2 |
70 |
1.3 |
2320±50 |
138 |
3 |
|
|
3 |
50 |
1.0 |
2050±50 |
115 |
7 |
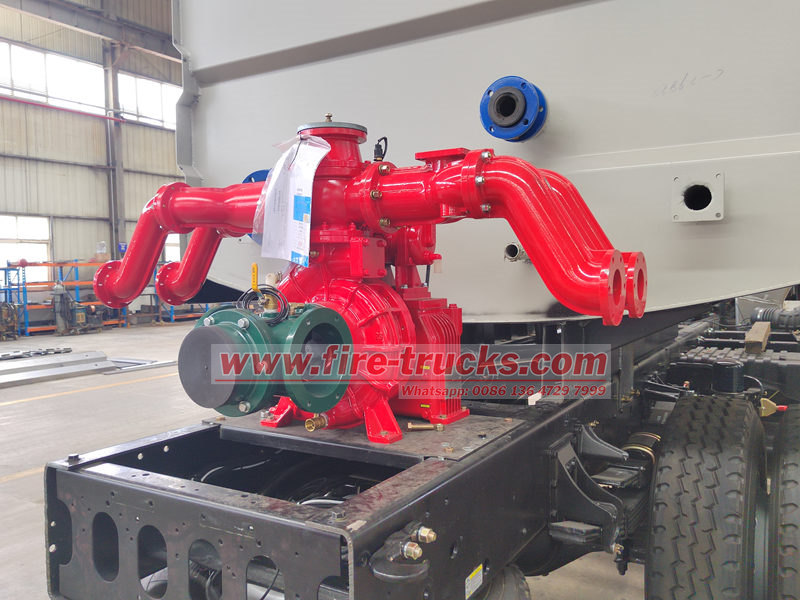

Queste pompe antincendio adottano un design centrifugo, offrendo elevata efficienza, stabilità e durata, soddisfacendo le esigenze operative di vari autopompe ISUZU.
2. Principio di funzionamento delle pompe antincendio
Le pompe antincendio installate sui camion ISUZU sono in genere pompe centrifughe, che funzionano sfruttando la forza centrifuga. Quando il motore aziona l'albero della pompa, la girante gira ad alta velocità, facendo fluire rapidamente l'acqua all'interno del corpo pompa. Grazie alla forza centrifuga, l'acqua viene spinta verso l'esterno, formando un flusso ad alta pressione che viene erogato attraverso l'uscita alle manichette antincendio o agli ugelli.
I vantaggi delle pompe centrifughe includono portate elevate, pressione stabile e idoneità al funzionamento continuo prolungato. Inoltre, le pompe antincendio ISUZU sono spesso dotate di sistemi di aspirazione assistita da vuoto, che consentono un rapido prelievo di acqua da fonti come idranti, serbatoi o corpi idrici naturali, migliorando i tempi di risposta. Alcuni modelli avanzati supportano anche il pompaggio multistadio, consentendo regolazioni di pressione e portata in base alle esigenze antincendio per massimizzare l'efficienza.
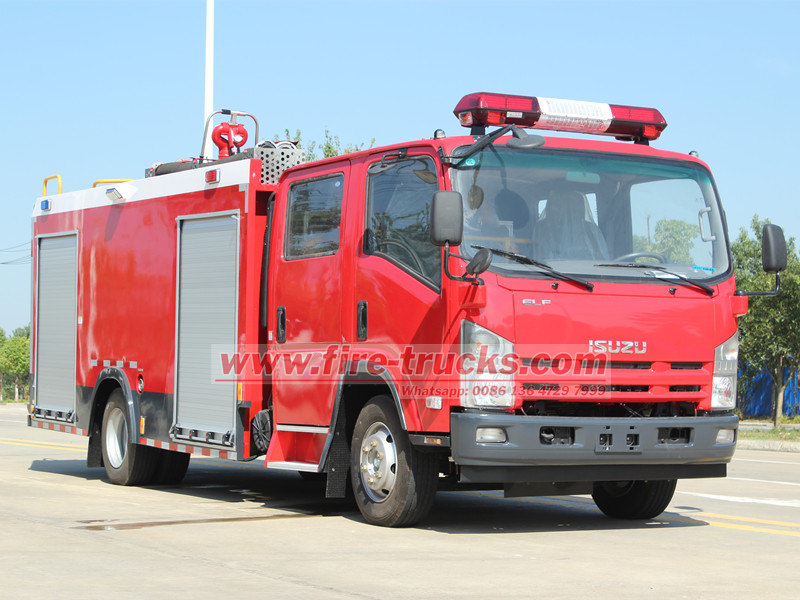

3. Manutenzione giornaliera delle pompe antincendio
Per garantire il funzionamento stabile a lungo termine dei camion antincendio ISUZU, la manutenzione regolare della pompa antincendio è essenziale. Le principali procedure di manutenzione includono:
(1) Ispezioni regolari delle guarnizioni
I componenti di tenuta (ad esempio, tenute meccaniche, O-ring) possono usurarsi nel tempo, causando perdite o cali di pressione. Dopo ogni utilizzo, ispezionare il corpo della pompa per individuare eventuali perdite e sostituire periodicamente le guarnizioni.
(2) Lubrificazione dei cuscinetti e dei componenti della trasmissione
I cuscinetti e l'albero motore della pompa antincendio richiedono una lubrificazione regolare per ridurre l'attrito e l'usura. In genere, si consiglia di eseguire la lubrificazione ogni 500 ore di funzionamento o ogni sei mesi.
(3) Prevenzione del congelamento della pompa (manutenzione invernale)
Nei climi freddi, l'acqua residua nella pompa potrebbe congelare, causando crepe. Dopo l'uso, scaricare tutta l'acqua dalla pompa o aggiungere antigelo per proteggerla.
(4) Test di prestazione regolari
Eseguire un test di funzionamento della pompa antincendio ogni tre mesi per verificarne portata e pressione. Se si rilevano anomalie, riparare o sostituire tempestivamente le parti usurate.

4. Come scegliere la pompa antincendio ISUZU giusta?
Quando si sceglie una pompa antincendio per un camion dei pompieri ISUZU, bisogna considerare i seguenti fattori:
• Requisiti antincendio: la lotta antincendio in comunità su piccola scala potrebbe richiedere CB10/20 o CB10/30, mentre le grandi zone industriali o la lotta antincendio in aeroporti richiedono pompe ad alta portata come CB10/80 o CB10/100.
• Capacità di carico del telaio: i telai ISUZU NPR leggeri sono adatti per piccole pompe, mentre i telai ISUZU GIGA per impieghi gravosi possono ospitare pompe ad alta portata.
• Condizioni della fonte d'acqua: se la fonte d'acqua è distante o ha una bassa pressione, optare per una pompa antincendio ad alta aspirazione con un sistema assistito dal vuoto.
Le autopompe ISUZU, con la loro eccellente mobilità e i sistemi di pompaggio affidabili, sono risorse vitali per i vigili del fuoco di tutto il mondo. Conoscere le caratteristiche, i principi di funzionamento e i metodi di manutenzione dei diversi modelli di pompe antincendio contribuisce a migliorare l'efficienza operativa e a prolungare la durata utile delle autopompe. Che si tratti di un'autopompa ISUZU leggera, media o pesante, la scelta della pompa antincendio giusta e la corretta manutenzione garantiscono prestazioni ottimali in situazioni critiche, salvaguardando vite umane e beni.

Potresti essere interessato alle seguenti informazioni